38 how to read uk nutrition labels
Nutrition Facts Labels - How to Read - For Kids - Dr. Smarty Nutrition Facts Labels - How to Read - For Kids - Animation for American Nutrition facts labels explained. › government › publicationsTechnical guidance on nutrition labelling - GOV.UK This technical guidance provides informal, non-statutory advice for businesses on the nutrition-related requirements of EU Regulation No. 1169/2011 on the provision of food information to consumers...
Nutrition labelling | Food Standards Agency Nutrition information must be expressed per 100 g/ml, using the measurement units specified in Regulation 1169/2011 vitamins and minerals must be expressed per 100g/ml and as a percentage of the...

How to read uk nutrition labels
› understanding-food-labelsUnderstanding food labels | Diabetes UK The labels show how many calories are in the food or drink and are also colour coded to show whether the food is low (green), medium (amber) or high (red) in fat, saturated fat, sugar and salt. The information on the front of the pack also tells you how the portion of the food contributes to the Reference Intake (RI) of an adult. Food labels - Coeliac UK Gluten free labelling. There is a law that covers the use of the labelling term gluten free. When you see gluten free on a label, you know these foods are suitable on a gluten free diet. The term 'gluten free' is covered by law and can only be used on foods which contain 20 parts per million (ppm) or less of gluten. You might see this on ... archive.nutrition.org.ukHome - British Nutrition Foundation The British Nutrition Foundation is a registered charity. We provide impartial, evidence-based information, resources and training on food and nutrition. BNF's vision is 'Everyone can access healthy, sustainable diets' and it is contributing towards this through its Mission ‘Translating evidence-based nutrition science in engaging and actionable ways’.
How to read uk nutrition labels. How to understand food labels - Eat For Health The Nutrition Information Panel on a food label offers the simplest and easiest way to choose foods with less saturated fat, salt (sodium), added sugars and kilojoules, and more fibre. It can also be used to decide how large one serve of a food group choice or discretionary food would be and whether it's worth the kilojoules. How To Read Nutrition Labels Like a Dietitian [Infographic] You check the nutrition label on a product, and you notice it has some added sugar. However, you take a look at the ingredient list, and sugar is nowhere to be found. There are several types of sweeteners and sugars that manufacturers use to produce their products. Check out the names for some of the most common: Sucrose High fructose corn syrup How to Read a Nutrition Label Like You Actually Know What You're Doing Here's what R.D.s say you should really pay attention to on a label: RELATED: 7 Women Share the Cooking Disasters That Made Them Question Everything Zoom in on Fiber › information-advice › healthHealthy eating guide | Age UK Looking at the food labels found on most pre-packaged foods can help you make healthy choices. Try to get in the habit of reading pack labels and comparing brands before you buy. What information should be on a food label? Food labels can help you see which foods are high in fat, salt and added sugars.
How To Read Nutrition Labels (Like a Pro) - Ditch The Carbs Firstly you need to understand the difference between total and net carbs. TOTAL CARBS = sugars + starches +fibre NET CARBS = total carbs - fibre Carbohydrates will be on the nutrition label are often broken down into carbohydrates, sugars, starch, and fiber. However, each brand may display its nutritional contents differently. PDF Technical guidance on nutrition labelling - GOV.UK 2. Dates of application of nutrition labelling provisions . Application dates . EU FIC will make nutrition labelling mandatory for the majority of pre-packed foods from 13 December 2016. If you provide a nutrition declaration on a voluntary basis before 13 December 2016, it must still comply with the nutrition labelling provisions of EU FIC. How to Understand and Use the Nutrition Facts Label | FDA When looking at the Nutrition Facts label, first take a look at the number of servings in the package (servings per container) and the serving size. Serving sizes are standardized to make it easier... Looking at labels - British Nutrition Foundation Using the government scheme, a combination of colour coding (traffic lights) and nutritional information is used to show, at a glance, whether a product is high (red), medium (amber) or low (green) in fat, saturated fat, salt and sugars, and how much energy (calories and kilojoules) it provides.
Nutrition labels - Food A Fact Of Life High, medium or low - applying traffic light labelling to recipes; Nutrition labels worksheet - analyse a recipe a complete the back of pack nutrition information. Provide the pupils with the clean packaging from a range of standard and healthy option foods. Task the pupils to read and compare the food labels and discuss the findings. Nutrition information on food labels: Is it read and understood? In Europe, the provision of such information is not compulsory, unless a nutrition or health claim is made. However, a recent EU-funded research project, FLABEL (Food Labelling to Advance Better Education for Life) has shown that on average 85% of products contained nutrition information on the back of the pack and around 48% on the front. 1. This Is How to Read a Nutrition Facts Label on the Keto Diet The Basics of Reading Food Labels: How to Read a Label in 5 Steps (For Any Diet) To make healthy food choices, stick to these five steps. Step #1: Check the Serving Size. Always start by looking at its serving size. This will ensure that you're calculating nutrition based on the amount of food you're actually consuming. How to Read a Nutrition Label | Kellogg's Toward the bottom of each label you'll find the percentage of vitamins and minerals that accompany every serving, with a higher percentage indicating that there is more of a vitamin or mineral in that food. These vitamins and minerals serve many functions in your body. And to help keep it working properly, you need a variety of these nutrients.
› government › publicationsNutrition legislation information sources - GOV.UK Dec 19, 2014 · The nutrition information legislation sheet has been updated at section 5 to reflect the new Delegated Regulation (EU) 2016/127 on infant and follow-on formula, which came into force on 22 ...
Check the label | Food Standards Agency Watch on The traffic light labelling system will tell you whether a food has high, medium or low amounts of fat, saturated fat, sugars and salt. It will also tell you the number of calories and...
› healthy-sustainable-dietsProtein - British Nutrition Foundation Protein on food labels. The protein content of a food is among the mandatory information to be provided in the nutrition declaration on food labels, according to Regulation (EU) No. 1169/2011. For labelling purposes, the reference intake for protein of an average adult (8400kJ/2000kcal) is 50g/day.
Food labelling - get into the habit of checking the label Look for five key points on the label: 1. Energy The terms 'kJ' and 'kcal' (calories) tell you how much energy is in a product. Women need an average of 2,000 kcal a day and men need 2,500 kcal on average. 2. Saturates Saturates is another word for saturated fat. This section tells you about the amount of saturated fat in the product. 3. Salt
Food labelling - British Nutrition Foundation Food labelling We aim to give people access to reliable science-based information to support anyone on their journey towards a healthy, sustainable diet. In this section you can read about the information you can find on food labels, including nutrition labelling and nutrition and health claims. Enlarge Text Looking at labels
How to read a food nutrition label (correctly) | GQ India How to read a food nutrition label accurately: Serving size The label starts with the total number of servings per container, for this specific food. This is not a recommendation of how much of the...
How to Read Carbohydrates on Food Labels - GlycoLeap That would be around 15 to 30 g of carbohydrates. Snack = 15 - 30 g of carbohydrate. For the main meals (breakfast, lunch, dinner), 2 to 3 servings of carbs would be enough. That is about 30-45 g of carbohydrates. 3 servings of carbohydrates are about the size of 1 fist size of rice.

How to Read a Nutrition Label | Reading food labels, Nutrition facts label, Nutrition labels
10 tips for understanding food labels - Heart Matters magazine Here are 10 easy tips to help you read back-of-packet labelling: 1. Read the ingredients list Most pre-packaged foods have an ingredients list on the back of the packet. Everything that goes into your food will be listed in weight order from biggest to the smallest.
Reading labels | Diabetes UK Key points. Always look at the 'total carbohydrate' on the label when carb counting. This will make sure you are counting both the complex (starchy) and simple (sugary) carbs in your food. Both will raise your blood glucose (blood sugar) levels, and need to be matched with insulin. In general, sugar-free options like diet drinks and jellies don't ...
Learn How to Read Supplement Labels With These Tips - CNET How to read dietary supplement labels. You will find the supplement facts label on the bottle or box of the supplement. Below, we've covered each area of a dietary supplement label so you'll know ...
Food labels - NHS Some front-of-pack nutrition labels use red, amber and green colour coding. Colour-coded nutritional information tells you at a glance if the food has high, medium or low amounts of fat, saturated fat, sugars and salt: red means high; amber means medium; green means low; In short, the more green on the label, the healthier the choice.
How to Read a Nutrition Label: The Path to More Empowered Eating Choices Nutrition and Percent Daily Value (DV) Remember that companies must disclose what their food provides you in nutrients. To figure this out, multiply the number of servings you consumed (or plan to consume) by the calories and grams of fat, sodium, sugar, and carbohydrates provided on the food label.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › LabelLabel - Wikipedia Labels have many uses, including promotion and providing information on a product's origin, manufacturer (e.g., brand name), use, safety, shelf-life and disposal, some or all of which may be governed by legislation such as that for food in the UK or United States.
Reading Nutrition Labels - Cronometer Serving sizes measured in grams, including a 100g serving size option Vitamin C, Vitamin A, Calcium, Iron %DV (based on 2000 kcal diet) This percentage is listed as the % of the RNI which is different than that of American targets. We will always report the numeric value (not the percent) in CRDB foods. Carbohydrates reported do NOT include fibre.
How to Read Nutrition Information → Food Labels EXPLAINED This video will teach you how to read nutrition labels properly. We'll go through a bunch of different nutrition labels and show you the specific things you should be looking for on a food label....


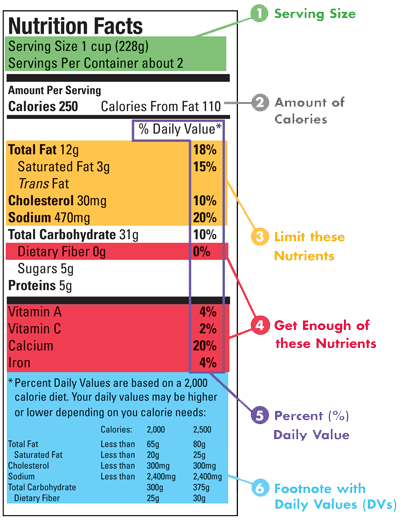





Post a Comment for "38 how to read uk nutrition labels"